Explaining Different Types of Proxy IPs: Shared, Dedicated, and Rotating IPs
In the contemporary landscape of the Internet, proxy IPs have emerged as vital tools for various network activities. They enable users to conceal their true IP addresses, ensuring anonymity, enhancing network security, and circumventing geographical restrictions. However, proxy IPs come in various types, each serving distinct purposes and offering unique functionalities. These types include shared IPs, dedicated IPs, and rotating IPs. This article aims to elucidate the definitions, features, suitable scenarios, and precautions associated with each of these proxy IP variants.
Shared IP
Shared IP is a proxy service where numerous users utilize a single IP address collectively. In this arrangement, all user requests routed through this IP share the same exit IP address, facilitating efficient cost distribution among users. This shared approach enables cost-effective utilization of resources, as expenses are divided among multiple users. Additionally, shared IPs can enhance anonymity by masking individual user identities behind a common exit IP address. However, users should be mindful of potential drawbacks such as reduced speed or the risk of being affected by the actions of other users sharing the same IP.
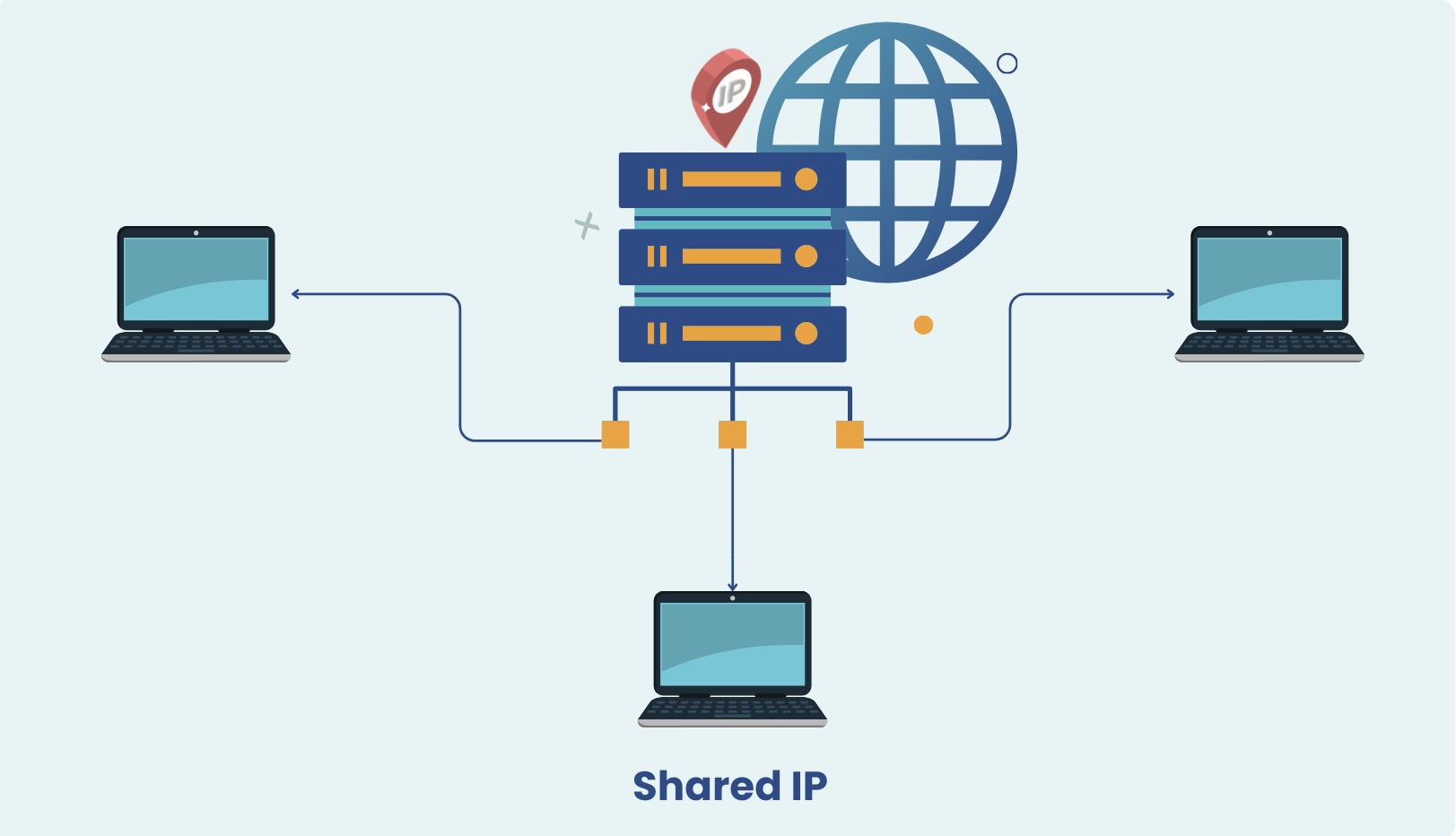
- Features
- Applicable scenarios
- Precautions
The primary characteristic of a shared IP is its cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for scenarios where numerous users require simultaneous access. With multiple users sharing the same IP address, the cost per user is comparatively lower. Furthermore, shared IPs offer considerable flexibility and scalability, allowing adjustment of the IP pool size according to user requirements at any given time. This adaptability ensures that resources can be tailored to accommodate fluctuating demands effectively.
Shared IP addresses are well-suited for situations where top-tier IP quality isn't essential, but a substantial quantity of IPs is necessary for various network activities like web crawling for data collection, SEO optimization endeavors, and online voting processes. In these instances, users prioritize the quantity and cost-effectiveness of IPs over their uniqueness and stability. This means that shared IPs cater to the needs of users who require a large volume of IP addresses for their operations, where the primary focus lies on cost efficiency rather than the exclusivity or reliability of the IP addresses.
Caution should be exercised when employing a shared IP address. Due to its shared nature among multiple users, there's a heightened risk of encountering bans or restrictions, as the IP address may be utilized frequently across different activities.
Furthermore, the speed and stability of a shared IP can be influenced by the usage patterns of other users sharing the same address. Therefore, in scenarios necessitating high-speed and stable connections, alternative types of proxy IPs may warrant consideration.
Dedicated IP
In contrast to a shared IP, a dedicated IP entails a proxy service that furnishes a solitary IP address exclusively designated for a single user or organization. In this proxy arrangement, users benefit from an independent IP address, affording them exclusive access to all resources associated with that IP. This setup guarantees the autonomy and security of network activities, as users operate within a dedicated IP environment tailored solely to their needs. Additionally, dedicated IPs offer enhanced reliability and consistency in performance, as they are not subject to fluctuations caused by shared usage or potential bans affecting shared IP addresses.

- Features
- Applicable scenarios
- Precautions
The primary characteristics of a dedicated IP include independence and high stability. With dedicated IPs, users operate within a segregated environment, eliminating the potential risks associated with sharing IPs among multiple users. This exclusivity ensures enhanced security and privacy for network activities. Additionally, dedicated IPs typically offer higher network speeds and superior connection stability compared to shared IPs, fulfilling users' requirements for high-speed and reliable connections.
Dedicated IP addresses are well-suited for scenarios demanding top-notch IP quality and unwavering stability, including online payment processing, e-commerce transactions, and account management tasks. In such critical activities, users prioritize the assurance that their network operations remain unaffected by others, ensuring data security and privacy are upheld. With dedicated IPs, users enjoy an isolated environment, minimizing the risk of interference from other users and bolstering the integrity of their online transactions. This heightened level of control and security is indispensable for safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring uninterrupted, secure online interactions.
It's essential to be aware that utilizing a dedicated IP entails a higher cost compared to shared IP services due to the exclusive access to IP resources provided to users. Additionally, users bear the responsibility of managing and maintaining their IP addresses independently to uphold both the security and availability of the IP. This includes implementing necessary security measures, such as regular monitoring and updates, to mitigate potential vulnerabilities and ensure uninterrupted access to the dedicated IP. Despite the higher cost and added management efforts, the enhanced control and security offered by dedicated IPs make them indispensable for applications where reliability and data protection are paramount.
Rotating IP
Rotating IP is a proxy service offered by providers who furnish users with a pool of IP addresses, which are automatically switched at regular intervals or based on predefined rules. This dynamic proxy method serves to mitigate the risk of individual IPs being blocked and enhances the likelihood of successful network activities. By cycling through a diverse range of IP addresses, rotating IP facilitates improved anonymity and resilience in online operations. Additionally, the automated rotation of IPs minimizes the need for manual intervention, streamlining the user experience and optimizing the effectiveness of proxy-based activities.
- Features
- Applicable scenarios
- Precautions
Rotating IP offers distinctive features, notably flexibility and heightened security. Through periodic changes in IP addresses, the service mitigates the likelihood of individual IPs being detected and blocked, thereby enhancing both anonymity and the success rate of network endeavors. Moreover, rotating IP solutions are adaptable to user preferences, allowing for customization of replacement strategies and frequencies tailored to specific requirements. This versatility empowers users to optimize their proxy usage according to the unique demands of their online activities, ensuring optimal concealment and operational efficiency. Additionally, the dynamic nature of rotating IPs provides an added layer of protection against potential threats, bolstering overall network security.
Rotating IP proves invaluable in scenarios necessitating frequent IP address changes for various network activities, such as web crawling for data collection and bulk registration of accounts. In these instances, users prioritize the imperative of evading detection and potential blocking by target websites, making IP rotation a strategic solution. By continually switching IP addresses, rotating IP offers a dynamic approach to circumventing detection and bolstering the success rate of such activities. This adaptive strategy is particularly beneficial for users engaged in tasks where maintaining anonymity and avoiding detection are paramount, ensuring seamless operation while minimizing the risk of disruptions or access restrictions.
While utilizing rotating IPs can decrease the likelihood of bans by regularly changing addresses, excessive alterations may raise red flags for target websites. Hence, users must exercise caution and select suitable replacement strategies and frequencies based on their specific circumstances. It's crucial to strike a balance between mitigating detection risks and avoiding overactivity that may trigger suspicion.
Moreover, the stability and speed of rotating IPs may suffer during the replacement process, potentially impacting user experience. Prior to implementation, thorough testing and evaluation are imperative to assess performance and ensure compatibility with intended applications. This proactive approach allows users to fine-tune settings, mitigate potential disruptions, and optimize the effectiveness of rotating IP usage
In conclusion, shared IP, dedicated IP, and rotating IP represent three prevalent categories of proxy IPs, each offering distinct attributes tailored to varying scenarios and requirements.
When selecting a proxy IP, users must carefully assess their unique circumstances and objectives to ensure seamless execution of network activities. Additionally, adherence to pertinent laws, regulations, and ethical guidelines is paramount to avoid potential complications and losses stemming from misuse of proxy IPs.
It is imperative for users to make informed decisions, considering factors such as cost, security, and performance when choosing among shared, dedicated, or rotating IPs. By aligning their choice with their specific needs and staying mindful of legal and ethical considerations, users can effectively harness the benefits of proxy IPs while minimizing associated risks.
