As online privacy concerns continue to grow, many individuals are seeking ways to protect their identities while browsing the web.The benefits of proxy servers extend beyond privacy protection, offering users a range of advantages for both personal and business use.
Before delving into the advantages, it's essential to understand what proxy servers are and how they operate. By grasping their functionality, users can select the most suitable proxies for their requirements and fully leverage their capabilities. Let's explore this further.
What is Proxy Server ?
A proxy server refers to a server that acts as an intermediary between the request made by clients, and a particular server for some services or requests for some resources.A proxy server is a dedicated computer or a software system running on a computer that acts as an intermediary between an endpoint device, such as a computer, and another server from which a user or client is requesting a service. The proxy server may exist in the same machine as a firewall server or it may be on a separate server, which forwards requests through the firewall.
Benefits of Proxy Server
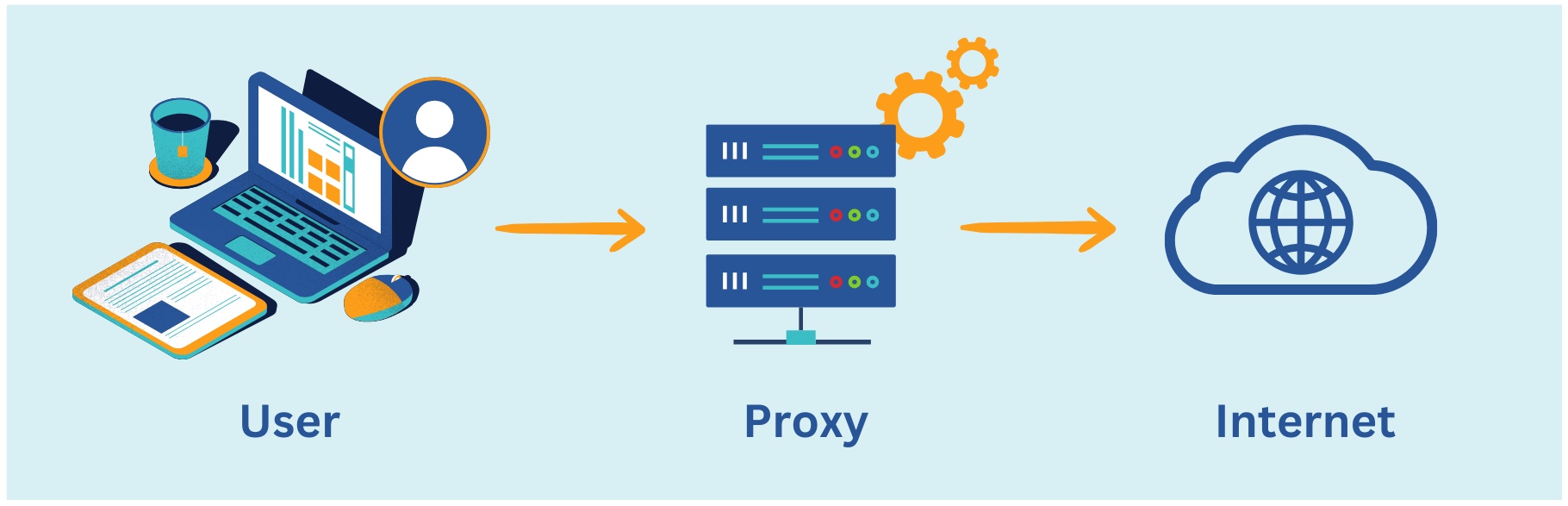
Proxy servers play a crucial role in managing and optimizing internet traffic by serving as intermediaries between users and web servers. The workings of a proxy server involve several key steps that facilitate this process.
Firstly, when a user sends a request for online content, it is intercepted by the proxy server before reaching the destination server. At this point, the proxy server evaluates the request and determines the appropriate action. It may choose to fulfill the request from its cache if the content has been previously accessed and stored, thereby speeding up the process and reducing bandwidth usage. If the content is not available in the cache or if caching is disabled, the proxy server forwards the request to the destination server on behalf of the user.
Secondly, the proxy server masks the user's identity and location by substituting its own IP address for the user's IP address in the outgoing request. This anonymization process enhances privacy and security by preventing the destination server from directly identifying and tracing the user. Additionally, proxy servers can implement various security measures such as content filtering, antivirus scanning, and intrusion detection to protect users from malicious content and cyber threats.
Thirdly, once the destination server processes the request, it sends back the response to the proxy server. The proxy server then relays this response to the user, completing the communication loop. Throughout this process, the proxy server may log information about the incoming and outgoing traffic for monitoring, analysis, and troubleshooting purposes. These logs can provide valuable insights into network activity and help administrators identify and address any issues or security threats.
Overall, the working of a proxy server involves intercepting and forwarding internet traffic, caching frequently accessed content, anonymizing user identities, implementing security measures, and logging network activity. By performing these functions, proxy servers enhance privacy, security, and efficiency in online communication for users and organizations alike.
Types of Proxies Based on the Direction of Traffic Flow
Types of proxies depend on different criteria, including traffic flow, application, anonymity level, service, etc. But we’re not going to discuss each one of them here. We’re only focusing on proxies based on the direction of traffic flow, which can either be forward or reverse.
Let’s start by discussing forward proxies.
Forward Proxy
A forward proxy, also known as simply a proxy server, is typically deployed within an internal network to manage outbound internet traffic. When a client within the network initiates a request to access a web resource, the request is forwarded to the forward proxy server. The proxy server then evaluates the request and, based on predefined rules and configurations, either fulfills the request by fetching the resource from the internet or blocks it, acting as a gateway between the internal network and the internet.
Datacenter proxies, on the other hand, are IP addresses provided by data centers. They are not associated with a specific physical location or ISP, making them less authentic compared to residential proxies. However, datacenter proxies are generally faster, more affordable, and easier to obtain in bulk. They are commonly used for tasks that prioritize speed and scalability over anonymity, such as SEO monitoring, ad verification, and market research.
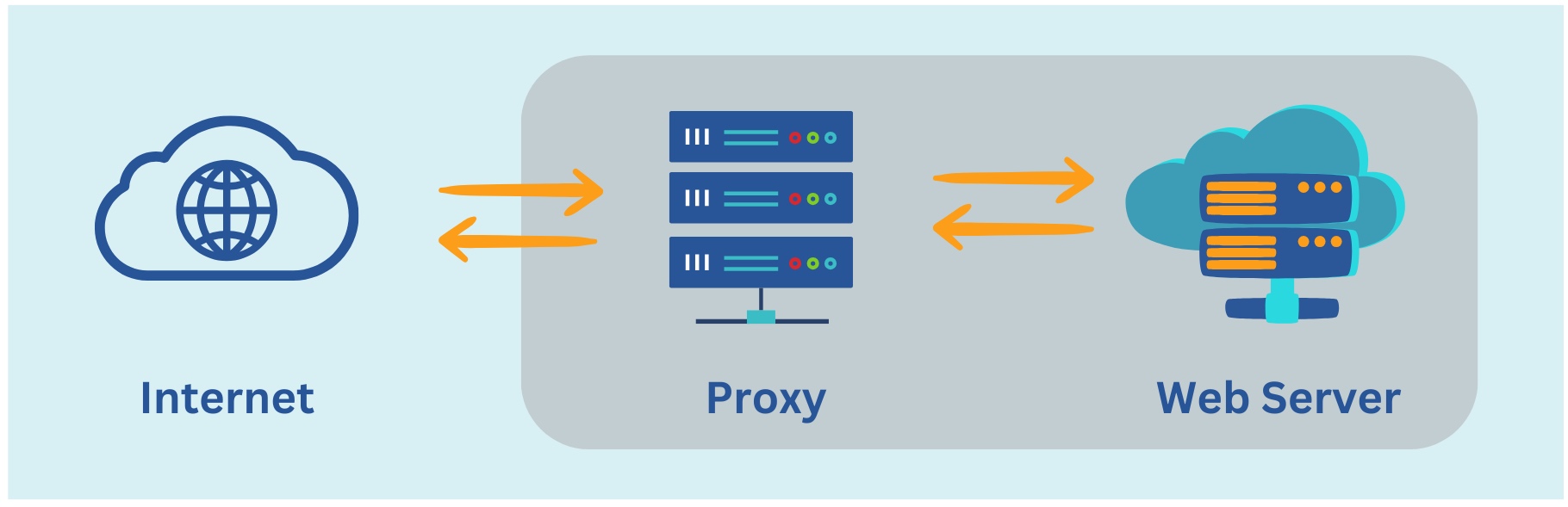
Reverse Proxy
Contrary to a forward proxy, a reverse proxy sits in front of web servers and handles incoming client requests on behalf of those servers. When a client sends a request to access a web application or service, it is intercepted by the reverse proxy, which then forwards the request to the appropriate backend server. Upon receiving the response from the server, the reverse proxy relays it back to the client. This architecture effectively hides the backend servers from external clients, providing an additional layer of security and load balancing.
The Benefits of Using a Proxy Server
Employing a proxy server offers numerous benefits for both individuals and businesses. By substituting your IP address with another, you can gain unrestricted internet access, enhancing your anonymity and security. Let's explore the significant advantages of employing reliable proxy servers for private and business users.
In today's digital era, safeguarding online privacy is paramount, especially with the pervasive tracking of user data by companies. Proxy servers play a crucial role in maintaining anonymity by concealing your IP address and location, making it challenging to track your online activities. This is particularly valuable for businesses, journalists, researchers, and NGOs, empowering them to freely express themselves, access essential information, and conduct online tasks securely and efficiently.
Geo-blocking often restricts access to online content based on geographic location, hindering users from accessing desired resources. Whether imposed by content providers or governments, geo-restrictions can be circumvented with proxies. By obtaining an IP address from a different location, proxies enable users to bypass these restrictions, granting access to content otherwise unavailable in their region.
In an increasingly perilous digital landscape, businesses must prioritize cybersecurity to mitigate the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches. Proxies offer an additional layer of security by operating at the application layer of the OSI model, minimizing the risk of data leaks and serving as effective firewalls or web filters against malware and other online threats. Private internet users can also benefit from proxies to safeguard sensitive data and prevent identity theft.
Automating data gathering through web scraping facilitates tasks such as market research and lead generation. However, IP-based restrictions imposed by websites can hinder scraping activities. Proxies enable circumvention of these restrictions by routing requests through different IP addresses, making it difficult for target servers to detect and block scraping activities.
Monitoring search engine results and analyzing competitors' SEO strategies are integral to enhancing online visibility and organic traffic. Proxies simplify this process by allowing businesses to replicate searches using multiple IPs from various locations, providing valuable insights to refine their SEO strategies and improve search engine rankings.
Proxies can accelerate content delivery and reduce bandwidth usage by caching frequently accessed content. This feature is particularly advantageous for corporate networks, improving page loading speed and reducing operational costs.
Business owners can use proxies to restrict access to distracting or harmful websites during office hours, enhancing productivity and protecting corporate data. Proxies facilitate the blocking of specific URLs or entire websites, enabling network administrators to enforce usage policies effectively.
Disadvantages of Proxy Server
While proxies can provide numerous benefits, they also come with potential cybersecurity risks, particularly those obtained from free and shared sources. Opting for shared proxies from unreliable providers may compromise online security, privacy, and speed.
One prevalent concern is the absence of encryption, unlike VPNs, which offer robust encryption protocols. This lack of encryption in proxies can leave connections vulnerable to interception, posing a significant risk to sensitive data. Additionally, proxies operating on open ports may inadvertently expose networks to cybercriminals, facilitating unauthorized access to confidential information.
Another drawback of free proxies is their inconsistent speed and propensity for frequent crashes. Reliability is crucial when relying on proxy servers for protection, necessitating the use of premium private proxies from reputable providers. By investing in premium services, users can ensure consistent performance and maximize the benefits of proxy usage while minimizing associated risks.
